Did you know that more than 150 million people in the world need walking assistance to move around? And that 30% of people aged over 65 suffer from walking disorders (200 million) suffers from walking disorders? (1) (2)
Whether it is due to a muscular or joint deficit, these people face daily difficulties to perform simple activities such as getting up, walking or climbing stairs.
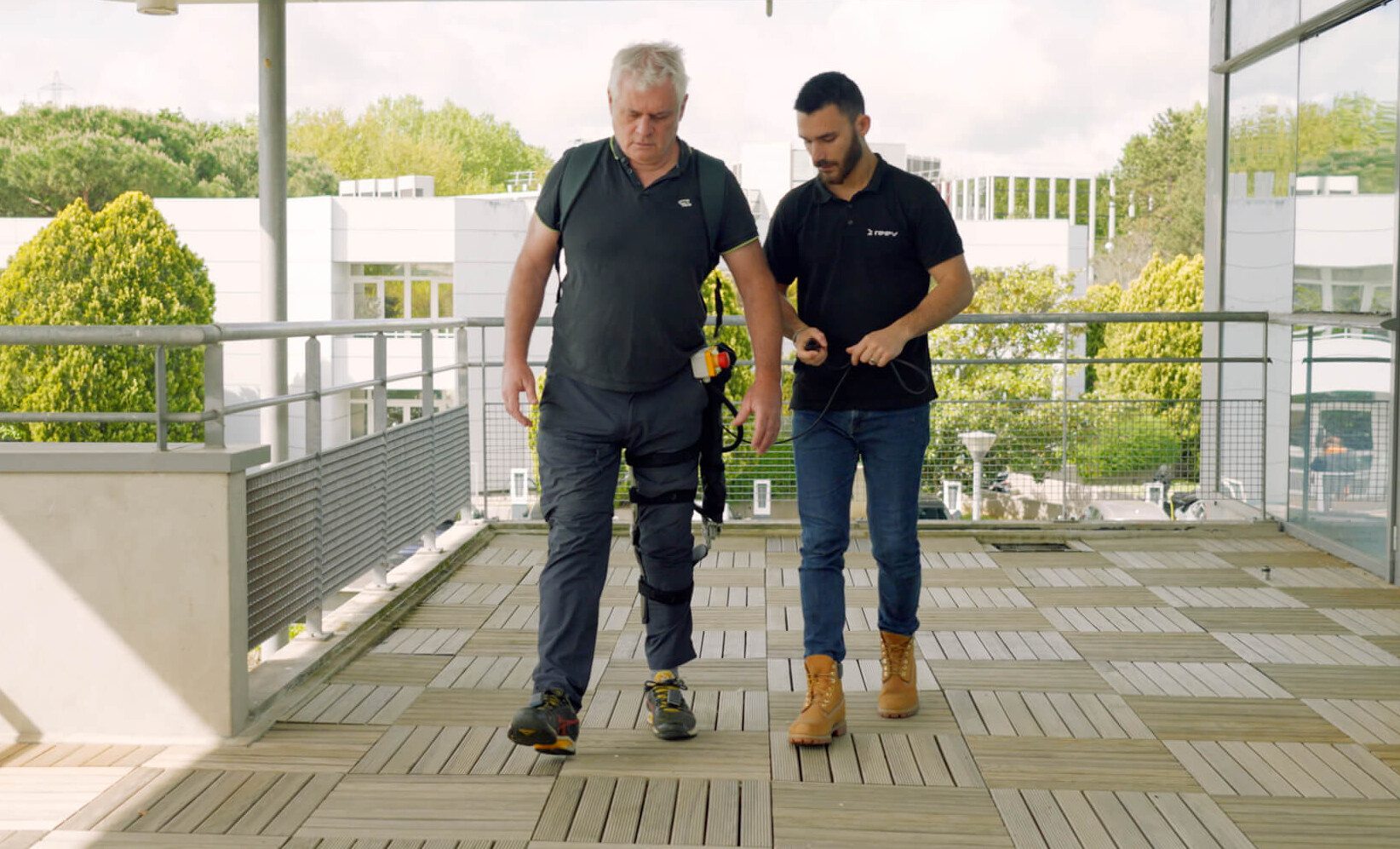
To remedy this, recent technological advances such as motorized assistance exoskeletons help affected people gain mobility and improve their autonomy and physical independence.
In this article, we will explain what an exoskeleton is, how it works, what are the benefits of exoskeletons and how they can help you gain freedom and confidence in your daily life.
What is an exoskeleton and how does it work?
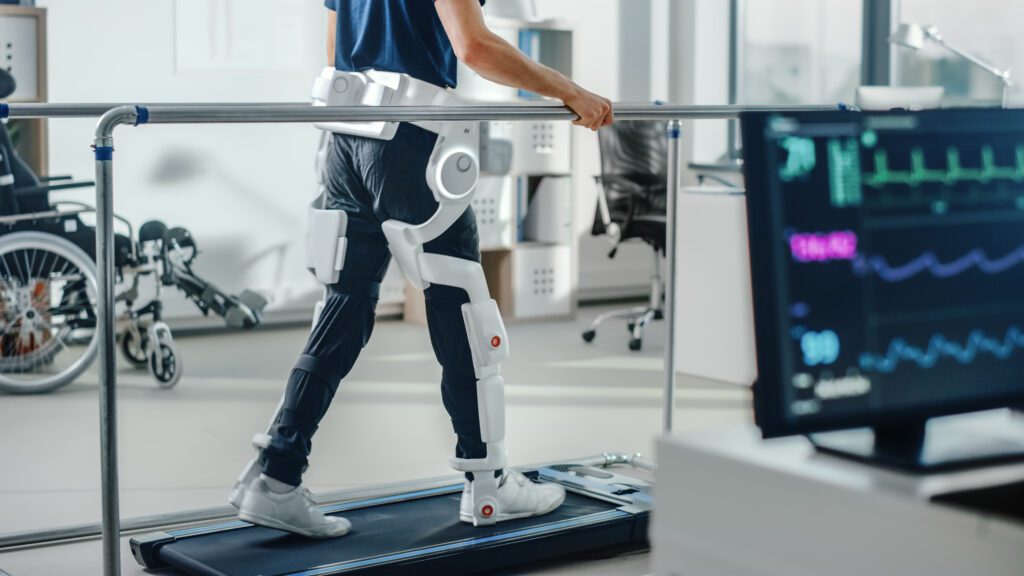

An exoskeleton is a physical assistance device that attaches to the user’s body. It consists of sensors, motors, batteries and software that allow it to detect the user’s movements and amplify or correct them. The exoskeleton thus helps the user to walk, stand up, carry heavy objects or perform specific tasks.
The market for exoskeletons is booming, especially in the medical sector where they are used for rehabilitation or assistance of people with reduced mobility. According to a market study by Fortune 2 , the global market for exoskeletons is expected to reach $12 billion by 2029, with an average annual growth rate of 43.6%.
The main factors that drive this market are the aging of the population, the increase of chronic diseases such as strokes or multiple sclerosis and the technological advances that make exoskeletons more efficient, comfortable and affordable.
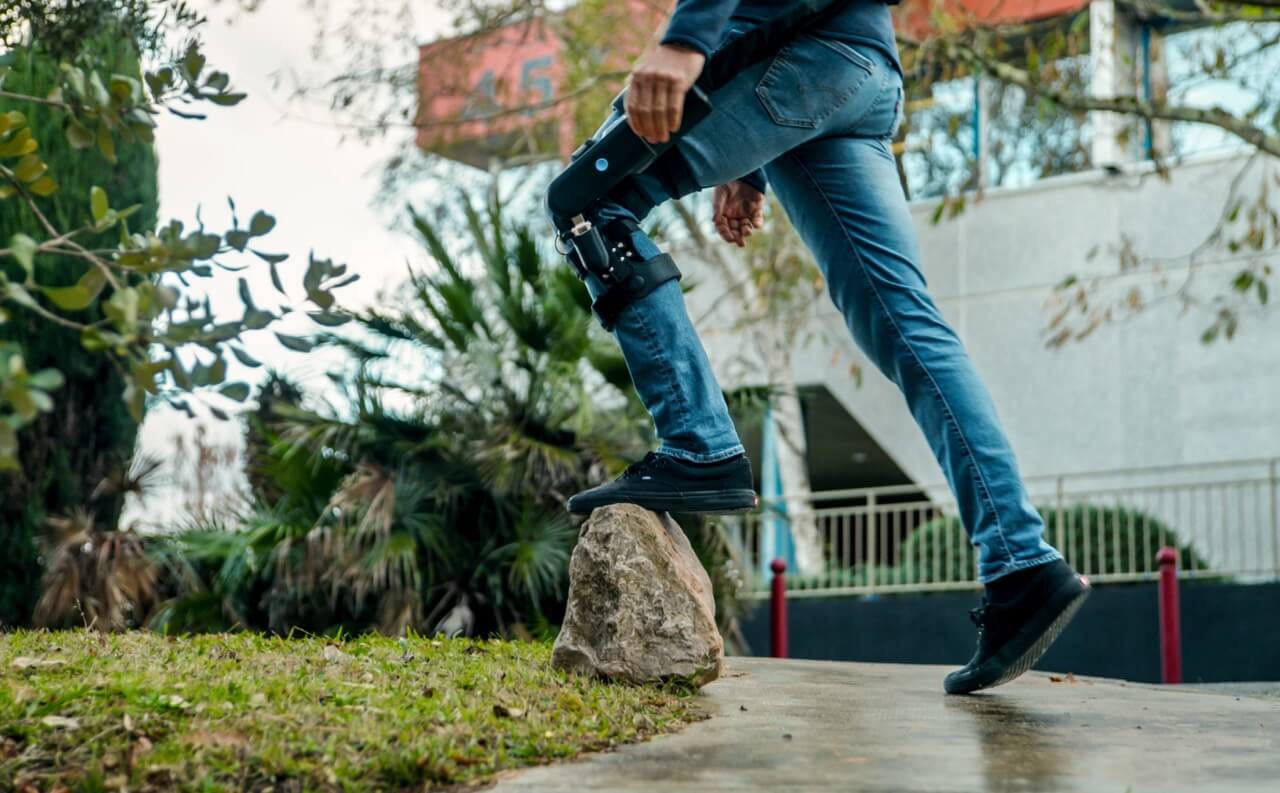
There are different types of exoskeletons according to their size, weight, autonomy, control mode and application. We can distinguish full exoskeletons that cover the whole body, partial exoskeletons that target a part of the body such as legs or arms, and motorized orthoses that are lighter and more discreet exoskeletons that support a joint such as knee or ankle.
Exoskeletons can be controlled by muscle signals (myoelectric), by external sensors (accelerometers) or by a remote control (manual). Exoskeletons can have various applications such as rehabilitation, assistance, sport, leisure or work.
The benefits of exoskeletons

Exoskeletons have many advantages over traditional walking aids such as crutches or mechanical orthoses. Here are some of these advantages:
- Exoskeletons improve mobility and autonomy of users who can move more easily and faster in different environments. They reduce the need for human assistance or additional equipment such as ramps or elevators.
- Exoskeletons increase confidence and self-esteem of users who feel more active, more independent and more socially integrated. They contribute to their quality of life and personal fulfillment.
- Exoskeletons offer a more personalized and tailored experience to the needs and preferences of users. They can be adjusted according to the level of strength, fatigue or pain of the user, and offer different modes of operation depending on the activity performed.
- Exoskeletons allow maintaining a vertical and natural posture that promotes the proper functioning of organs and muscle efficiency. They prevent complications related to prolonged sitting such as pressure ulcers, urinary infections or digestive disorders.
- Exoskeletons stimulate blood circulation and metabolism that are essential for general health and well-being.
The limitations of current exoskeletons:

However, exoskeletons are not without limitations or challenges. Among the main obstacles to their adoption, we can mention:
- The weight and size of exoskeletons that can be uncomfortable or inconvenient for the user or for people around them. Some exoskeletons can weigh up to 30 kg and require a large space to move around.
- The battery life that can be limited or variable depending on the use of the exoskeleton. Some exoskeletons can have an autonomy of only a few hours, which forces the user to recharge their device regularly or have a backup battery.
- The adaptation to the user that can be difficult or long depending on the type of exoskeleton and the profile of the user. Some exoskeletons require prior training or regular medical follow-up to be used correctly and safely.
- The cost that can be high or inaccessible for some users or some structures. Some exoskeletons can cost several tens of thousands of euros and not be reimbursed by social security or insurance.
Our mission at REEV
At REEV, our mission is to create a lightweight, discreet and intelligent exoskeleton that would be able to overcome the limitations of current exoskeletons and reach as many people as possible.
That’s why we are developing DREEVEN:
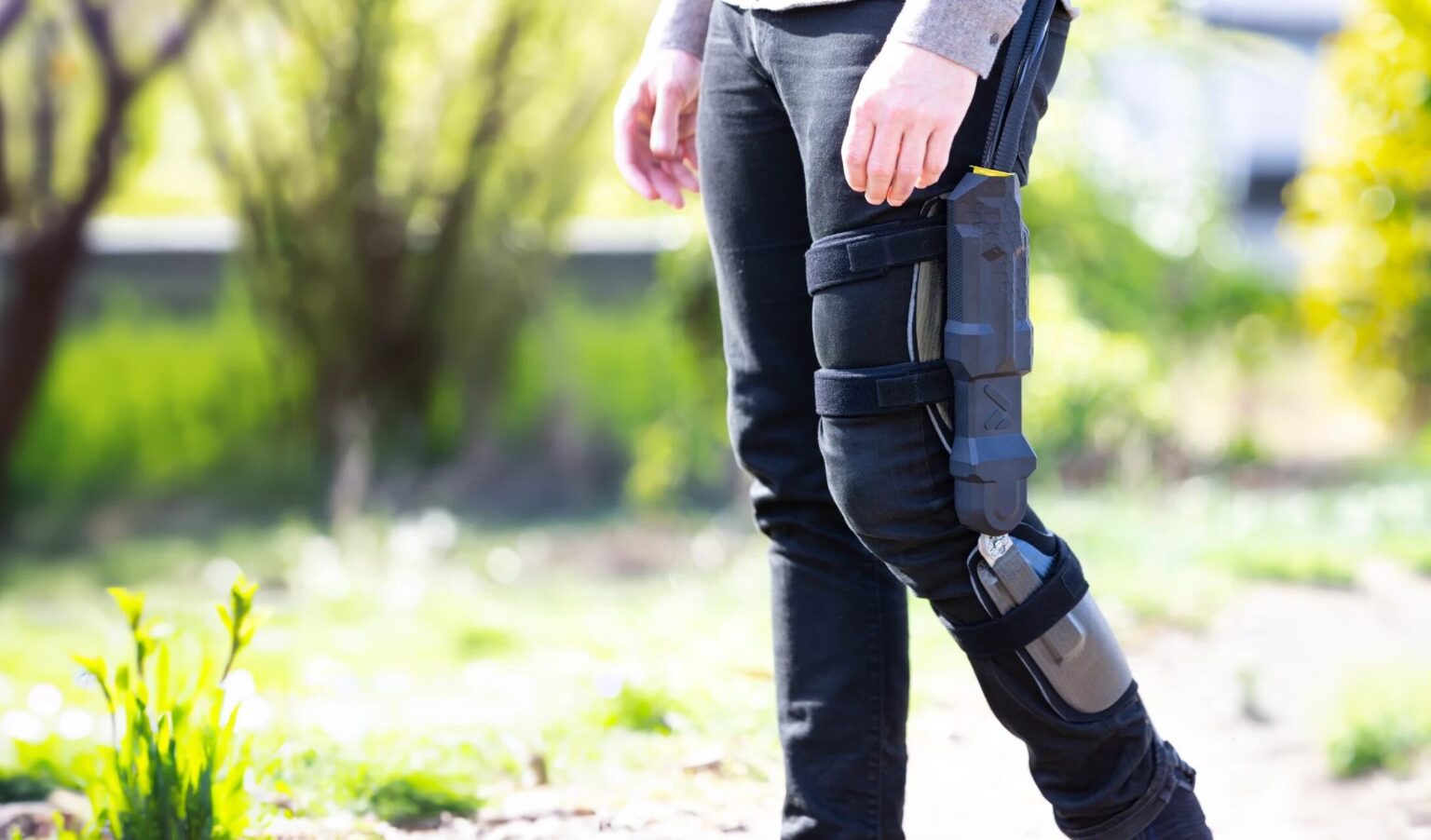

Our solution consists of a light motorization for medical orthosis coupled with artificial intelligence algorithms that provide personalized assistance to reduce the efforts required to walk, stand up, sit down or take stairs.
DREEVEN aims to facilitate daily movements at home or outdoors, for a duration of about 5 hours.